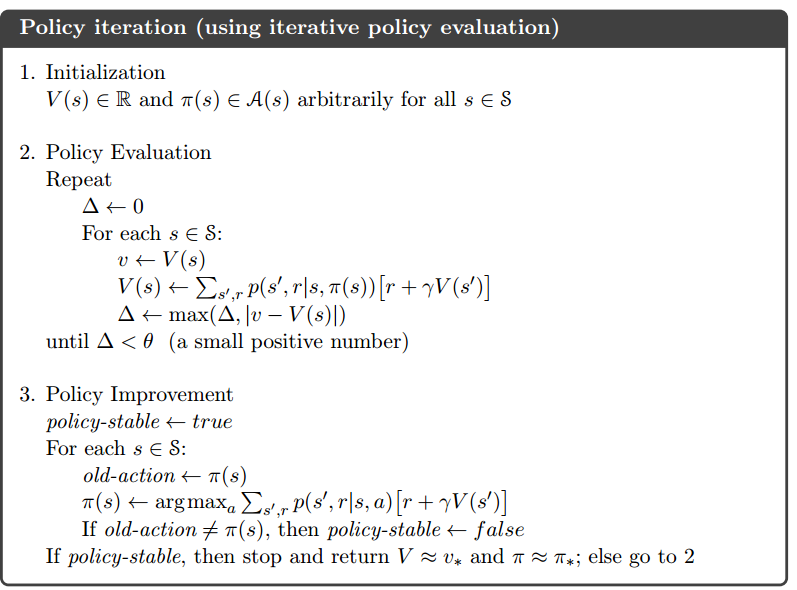
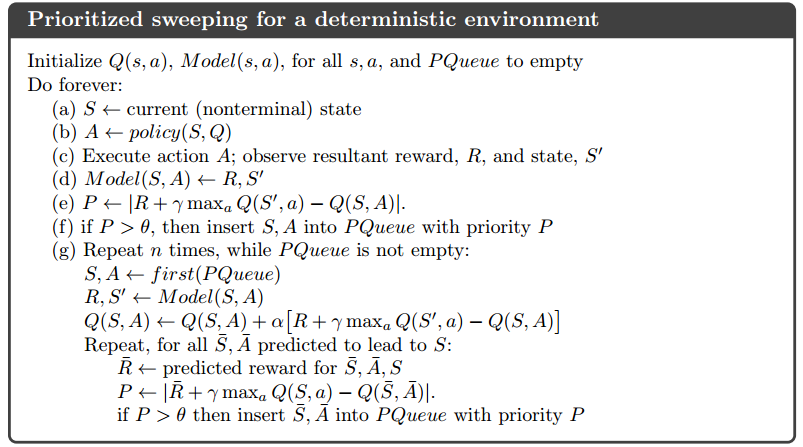
In this post, I am doing a brief code walkthrough for the code written in https://medium.com/emergent-future/simple-reinforcement-learning-with-tensorflow-part-8-asynchronous-actor-critic-agents-a3c-c88f72a5e9f2
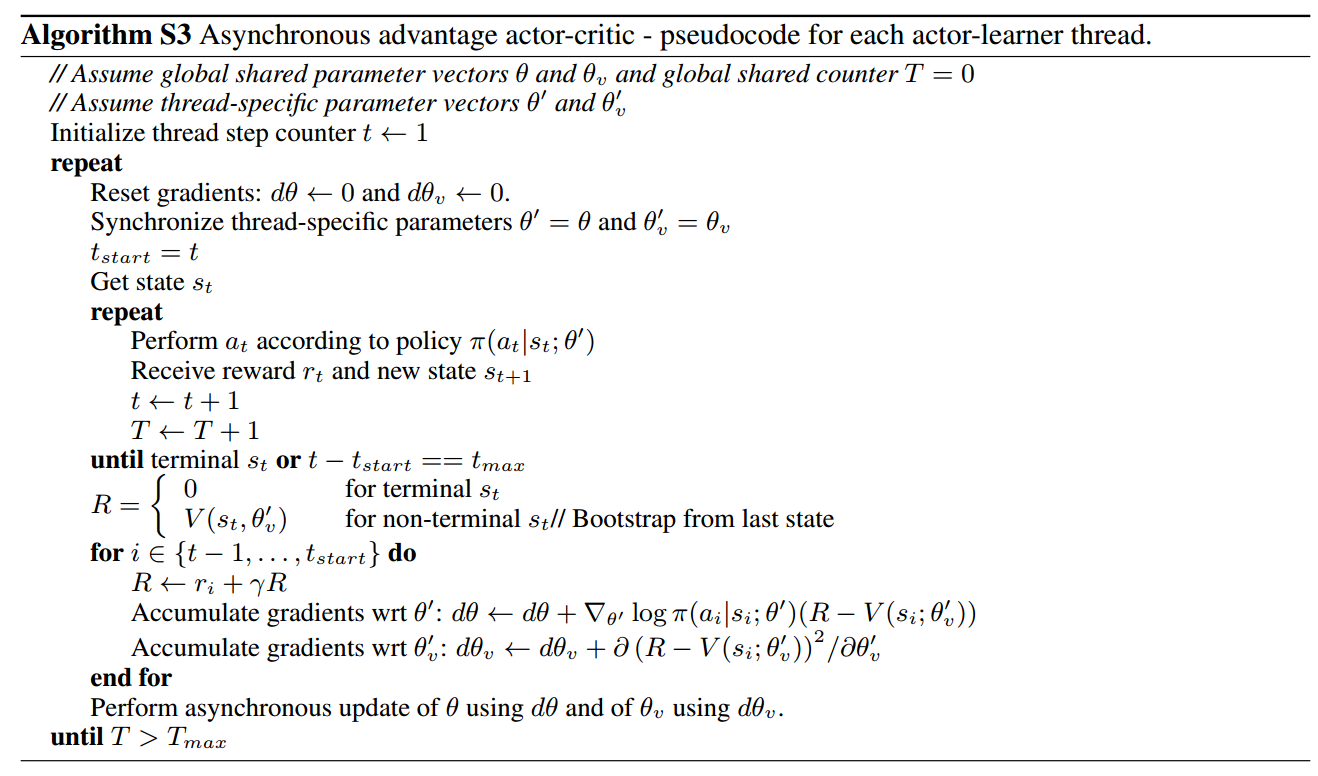
The code implements A3C algorithm (Asynchronous Methods for Deep Reinforcement Learning). It follows the pseudocode given in supplemental part in the paper:
The structure of this model is:
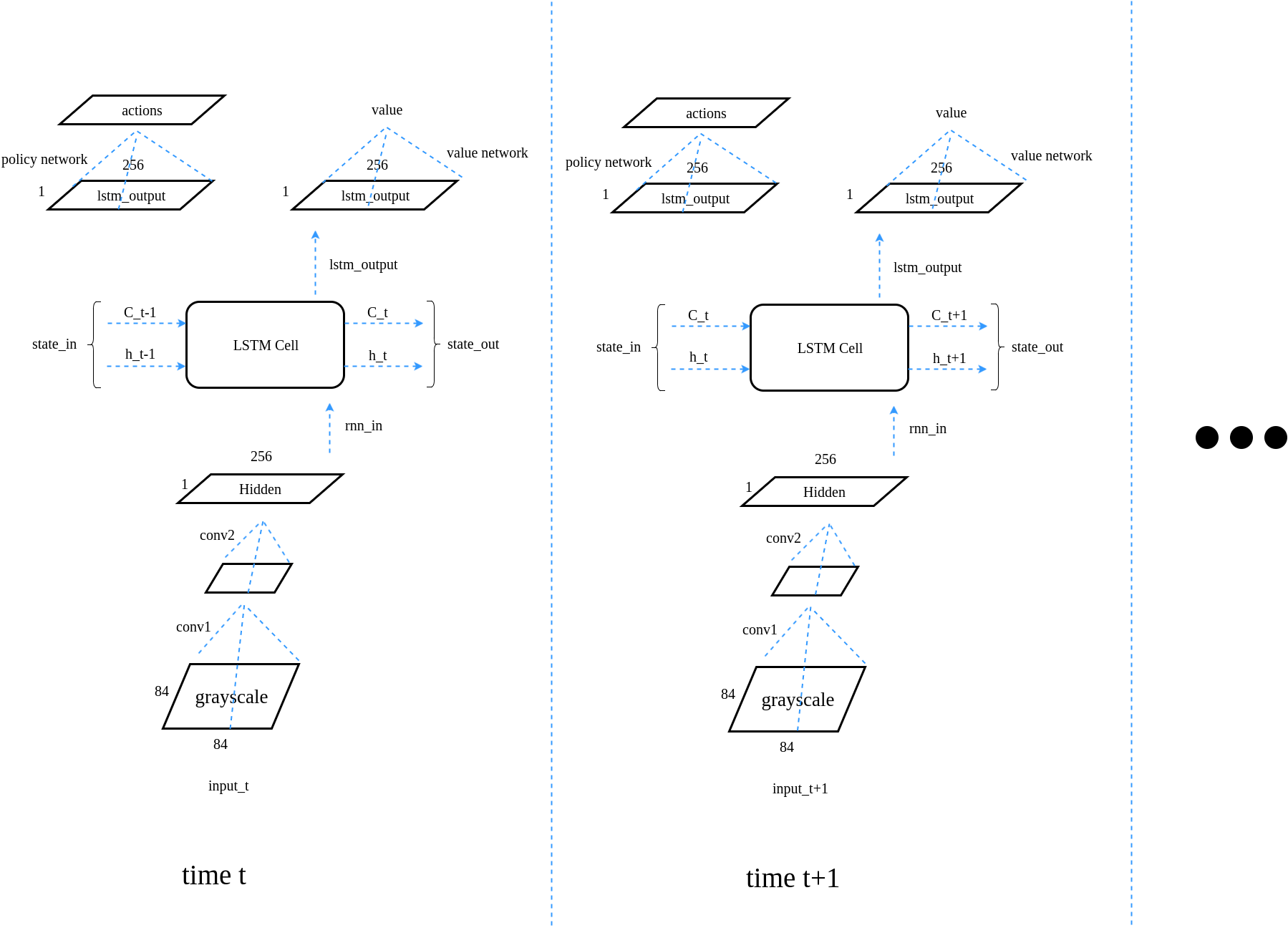
For LSTM structure detail, refer to http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/. I am using the same notation in the model structure diagram as in the link.
Below is the code:
"""
Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic algorithm
See:
https://medium.com/emergent-future/simple-reinforcement-learning-with-tensorflow-part-8-asynchronous-actor-critic-agents-a3c-c88f72a5e9f2
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1602.01783.pdf
"""
import copy
import threading
import multiprocessing
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim
import scipy.signal
from helper import *
from vizdoom import *
from random import choice
from time import sleep
from time import time
# Copies one set of variables to another.
# Used to set worker network parameters to those of global network.
def update_target_graph(from_scope,to_scope):
from_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, from_scope)
to_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, to_scope)
op_holder = []
for from_var,to_var in zip(from_vars,to_vars):
op_holder.append(to_var.assign(from_var))
return op_holder
# Processes Doom screen image to produce cropped and resized image.
def process_frame(frame):
s = frame[10:-10,30:-30]
s = scipy.misc.imresize(s,[84,84])
s = np.reshape(s,[np.prod(s.shape)]) / 255.0
return s
# Discounting function used to calculate discounted returns.
def discount(x, gamma):
return scipy.signal.lfilter([1], [1, -gamma], x[::-1], axis=0)[::-1]
#Used to initialize weights for policy and value output layers
def normalized_columns_initializer(std=1.0):
def _initializer(shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None):
out = np.random.randn(*shape).astype(np.float32)
out *= std / np.sqrt(np.square(out).sum(axis=0, keepdims=True))
return tf.constant(out)
return _initializer
class AC_Network():
def __init__(self, s_size, a_size, scope, trainer):
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
# Input and visual encoding layers
self.inputs = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, s_size], dtype=tf.float32)
self.imageIn = tf.reshape(self.inputs, shape=[-1, 84, 84, 1])
self.conv1 = slim.conv2d(activation_fn=tf.nn.elu,
inputs=self.imageIn, num_outputs=16,
kernel_size=[8, 8], stride=[4, 4], padding='VALID')
self.conv2 = slim.conv2d(activation_fn=tf.nn.elu,
inputs=self.conv1, num_outputs=32,
kernel_size=[4, 4], stride=[2, 2], padding='VALID')
hidden = slim.fully_connected(slim.flatten(self.conv2), 256, activation_fn=tf.nn.elu)
# Recurrent network for temporal dependencies
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(256, state_is_tuple=True)
self.lstm_cell_c_size = lstm_cell.state_size.c
self.lstm_cell_h_size = lstm_cell.state_size.h
c_init = np.zeros((1, lstm_cell.state_size.c), np.float32)
h_init = np.zeros((1, lstm_cell.state_size.h), np.float32)
self.state_init = [c_init, h_init]
c_in = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [1, lstm_cell.state_size.c])
h_in = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [1, lstm_cell.state_size.h])
self.state_in = (c_in, h_in)
rnn_in = tf.expand_dims(hidden, [0])
step_size = tf.shape(self.imageIn)[:1]
state_in = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMStateTuple(c_in, h_in)
lstm_outputs, lstm_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(
lstm_cell, rnn_in, initial_state=state_in, sequence_length=step_size,
time_major=False)
lstm_c, lstm_h = lstm_state
self.state_out = (lstm_c[:1, :], lstm_h[:1, :])
rnn_out = tf.reshape(lstm_outputs, [-1, 256])
# Output layers for policy and value estimations
self.policy = slim.fully_connected(rnn_out, a_size,
activation_fn=tf.nn.softmax,
weights_initializer=normalized_columns_initializer(0.01),
biases_initializer=None)
self.value = slim.fully_connected(rnn_out, 1,
activation_fn=None,
weights_initializer=normalized_columns_initializer(1.0),
biases_initializer=None)
# Only the worker network need ops for loss functions and gradient updating.
if scope != 'global':
self.actions = tf.placeholder(shape=[None], dtype=tf.int32)
self.actions_onehot = tf.one_hot(self.actions, a_size, dtype=tf.float32)
self.target_v = tf.placeholder(shape=[None], dtype=tf.float32)
self.advantages = tf.placeholder(shape=[None], dtype=tf.float32)
self.responsible_outputs = tf.reduce_sum(self.policy * self.actions_onehot, [1])
# Loss functions
self.value_loss = 0.5 * tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(self.target_v - tf.reshape(self.value, [-1])))
self.entropy = - tf.reduce_sum(self.policy * tf.log(self.policy))
self.policy_loss = -tf.reduce_sum(tf.log(self.responsible_outputs) * self.advantages)
self.loss = 0.5 * self.value_loss + self.policy_loss - self.entropy * 0.01
# Get gradients from local network using local losses
local_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope)
self.gradients = tf.gradients(self.loss, local_vars)
self.var_norms = tf.global_norm(local_vars)
grads, self.grad_norms = tf.clip_by_global_norm(self.gradients, 40.0)
# Apply local gradients to global network
global_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, 'global')
self.apply_grads = trainer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, global_vars))
def state_in_init(self):
c_init = np.zeros((1, self.lstm_cell_c_size), np.float32)
h_init = np.zeros((1, self.lstm_cell_h_size), np.float32)
self.state_init = [c_init, h_init]
class Worker():
def __init__(self, game, name, s_size, a_size, trainer, model_path, global_episodes):
self.name = "worker_" + str(name)
self.number = name
self.model_path = model_path
self.trainer = trainer
self.global_episodes = global_episodes
self.increment = self.global_episodes.assign_add(1)
self.episode_rewards = []
self.episode_lengths = []
self.episode_mean_values = []
self.summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("train_" + str(self.number))
# Create the local copy of the network and the tensorflow op to copy global paramters to local network
self.local_AC = AC_Network(s_size, a_size, self.name, trainer)
self.update_local_ops = update_target_graph('global', self.name)
# The Below code is related to setting up the Doom environment
game.set_doom_scenario_path("basic.wad") # This corresponds to the simple task we will pose our agent
game.set_doom_map("map01")
game.set_screen_resolution(ScreenResolution.RES_160X120)
game.set_screen_format(ScreenFormat.GRAY8)
game.set_render_hud(False)
game.set_render_crosshair(False)
game.set_render_weapon(True)
game.set_render_decals(False)
game.set_render_particles(False)
game.add_available_button(Button.MOVE_LEFT)
game.add_available_button(Button.MOVE_RIGHT)
game.add_available_button(Button.ATTACK)
game.add_available_game_variable(GameVariable.AMMO2)
game.add_available_game_variable(GameVariable.POSITION_X)
game.add_available_game_variable(GameVariable.POSITION_Y)
game.set_episode_timeout(300)
game.set_episode_start_time(10)
game.set_window_visible(False)
game.set_sound_enabled(False)
game.set_living_reward(-1)
game.set_mode(Mode.PLAYER)
game.init()
self.actions = np.identity(a_size, dtype=bool).tolist()
# End Doom set-up
self.env = game
def train(self, rollout, sess, gamma, bootstrap_value):
rollout = np.array(rollout)
observations = rollout[:, 0]
actions = rollout[:, 1]
rewards = rollout[:, 2]
next_observations = rollout[:, 3]
values = rollout[:, 5]
# Here we take the rewards and values from the rollout, and use them to
# generate the advantage and discounted returns.
# The advantage function uses "Generalized Advantage Estimation"
self.rewards_plus = np.asarray(rewards.tolist() + [bootstrap_value])
discounted_rewards = discount(self.rewards_plus, gamma)[:-1]
self.value_plus = np.asarray(values.tolist() + [bootstrap_value])
advantages = rewards + gamma * self.value_plus[1:] - self.value_plus[:-1]
advantages = discount(advantages, gamma)
# Update the global network using gradients from loss
# Generate network statistics to periodically save
rnn_state = self.local_AC.state_init
feed_dict = {self.local_AC.target_v: discounted_rewards,
self.local_AC.inputs: np.vstack(observations),
self.local_AC.actions: actions,
self.local_AC.advantages: advantages,
self.local_AC.state_in[0]: rnn_state[0],
self.local_AC.state_in[1]: rnn_state[1]}
v_l, p_l, e_l, g_n, v_n, _ = sess.run([self.local_AC.value_loss,
self.local_AC.policy_loss,
self.local_AC.entropy,
self.local_AC.grad_norms,
self.local_AC.var_norms,
self.local_AC.apply_grads],
feed_dict=feed_dict)
return v_l / len(rollout), p_l / len(rollout), e_l / len(rollout), g_n, v_n
def work(self, max_episode_length, gamma, sess, coord, saver):
episode_count = sess.run(self.global_episodes)
total_steps = 0
print("Starting worker " + str(self.number))
with sess.as_default(), sess.graph.as_default():
while not coord.should_stop():
# copy global network parameter to self parameter
sess.run(self.update_local_ops)
# when a new episode starts, C_0 & h_0 of LSTM are reset to zero
self.local_AC.state_in_init()
episode_buffer = []
episode_values = []
episode_frames = []
episode_reward = 0
episode_step_count = 0
d = False
self.env.new_episode()
s = self.env.get_state().screen_buffer
episode_frames.append(s)
s = process_frame(s)
rnn_state = self.local_AC.state_init
while self.env.is_episode_finished() == False:
# Take an action using probabilities from policy network output.
# after this step, a_dist shape (1,3), v shape (1,1),
# rnn_state: first array (C): (1, 256), second array (h): (1, 256)
a_dist, v, rnn_state = sess.run(
[self.local_AC.policy, self.local_AC.value, self.local_AC.state_out],
feed_dict={self.local_AC.inputs: [s],
self.local_AC.state_in[0]: rnn_state[0],
self.local_AC.state_in[1]: rnn_state[1]})
a = np.random.choice(a_dist[0], p=a_dist[0])
a = np.argmax(a_dist == a) # return the best action index
# see http://vizdoom.cs.put.edu.pl/tutorial and
# https://github.com/mwydmuch/ViZDoom/blob/3bdb16935668aa42bb14cc38ac397b8954999cca/doc/DoomGame.md
# for reward description
# the agent gets rewards for each action which is -1 for each time tick,
# -6 if he shots but misses, and 100 if he kills the monster
r = self.env.make_action(self.actions[a]) / 100.0 # make_action returns reward
# In this example, the episode finishes after 300 tics or when the monster gets killed
# ref: http://www.cs.put.poznan.pl/visualdoomai/tutorial.html#basic - Game Runtime
d = self.env.is_episode_finished()
if d == False:
s1 = self.env.get_state().screen_buffer
episode_frames.append(s1)
s1 = process_frame(s1)
else:
s1 = s
episode_buffer.append([s, a, r, s1, d, v[0, 0]])
episode_values.append(v[0, 0])
episode_reward += r
s = s1
total_steps += 1
episode_step_count += 1
# If the episode hasn't ended, but the experience buffer is full, then we
# make an update step using that experience rollout.
if len(episode_buffer) == 30 and d != True and episode_step_count != max_episode_length - 1:
# Since we don't know what the true final return is, we "bootstrap" from our current
# value estimation.
v1 = sess.run(self.local_AC.value,
feed_dict={self.local_AC.inputs: [s],
self.local_AC.state_in[0]: rnn_state[0],
self.local_AC.state_in[1]: rnn_state[1]})
v1 = v1[0, 0]
v_l, p_l, e_l, g_n, v_n = self.train(episode_buffer, sess, gamma, v1)
episode_buffer = []
sess.run(self.update_local_ops)
# original code does not update state_init:
# in train function, rnn_state is always set to self.state_init which are two zero numpy arrays
self.local_AC.state_init = copy.deepcopy(rnn_state)
if d == True:
break
self.episode_rewards.append(episode_reward)
self.episode_lengths.append(episode_step_count)
self.episode_mean_values.append(np.mean(episode_values))
# Update the network using the experience buffer at the end of the episode.
if len(episode_buffer) != 0:
v_l, p_l, e_l, g_n, v_n = self.train(episode_buffer, sess, gamma, 0.0)
# Periodically save gifs of episodes, model parameters, and summary statistics.
if episode_count % 5 == 0 and episode_count != 0:
if self.name == 'worker_0' and episode_count % 25 == 0:
time_per_step = 0.05
images = np.array(episode_frames)
make_gif(images, './frames/image' + str(episode_count) + '.gif',
duration=len(images) * time_per_step, true_image=True, salience=False)
if episode_count % 250 == 0 and self.name == 'worker_0':
saver.save(sess, self.model_path + '/model-' + str(episode_count) + '.cptk')
print("Saved Model")
mean_reward = np.mean(self.episode_rewards[-5:])
mean_length = np.mean(self.episode_lengths[-5:])
mean_value = np.mean(self.episode_mean_values[-5:])
summary = tf.Summary()
summary.value.add(tag='Perf/Reward', simple_value=float(mean_reward))
summary.value.add(tag='Perf/Length', simple_value=float(mean_length))
summary.value.add(tag='Perf/Value', simple_value=float(mean_value))
summary.value.add(tag='Losses/Value Loss', simple_value=float(v_l))
summary.value.add(tag='Losses/Policy Loss', simple_value=float(p_l))
summary.value.add(tag='Losses/Entropy', simple_value=float(e_l))
summary.value.add(tag='Losses/Grad Norm', simple_value=float(g_n))
summary.value.add(tag='Losses/Var Norm', simple_value=float(v_n))
self.summary_writer.add_summary(summary, episode_count)
self.summary_writer.flush()
if self.name == 'worker_0':
sess.run(self.increment)
episode_count += 1
max_episode_length = 300
gamma = .99 # discount rate for advantage estimation and reward discounting
s_size = 7056 # Observations are greyscale frames of 84 * 84 * 1
a_size = 3 # Agent can move Left, Right, or Fire
load_model = False
model_path = './model'
tf.reset_default_graph()
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
os.makedirs(model_path)
# Create a directory to save episode playback gifs to
if not os.path.exists('./frames'):
os.makedirs('./frames')
with tf.device("/cpu:0"):
global_episodes = tf.Variable(0, dtype=tf.int32, name='global_episodes', trainable=False)
trainer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=1e-4)
master_network = AC_Network(s_size, a_size, 'global', None) # Generate global network
num_workers = multiprocessing.cpu_count() # Set workers ot number of available CPU threads
workers = []
# Create worker classes
for i in range(num_workers):
workers.append(Worker(DoomGame(), i, s_size, a_size, trainer, model_path, global_episodes))
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=5)
with tf.Session() as sess:
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
if load_model == True:
print('Loading Model...')
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(model_path)
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
else:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# This is where the asynchronous magic happens.
# Start the "work" process for each worker in a separate threat.
worker_threads = []
for worker in workers:
worker_work = lambda: worker.work(max_episode_length, gamma, sess, coord, saver)
t = threading.Thread(target=(worker_work))
t.start()
sleep(0.5)
worker_threads.append(t)
coord.join(worker_threads)
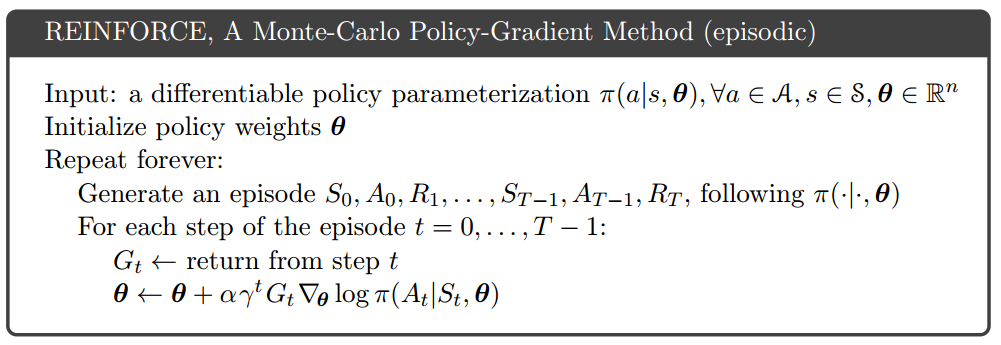
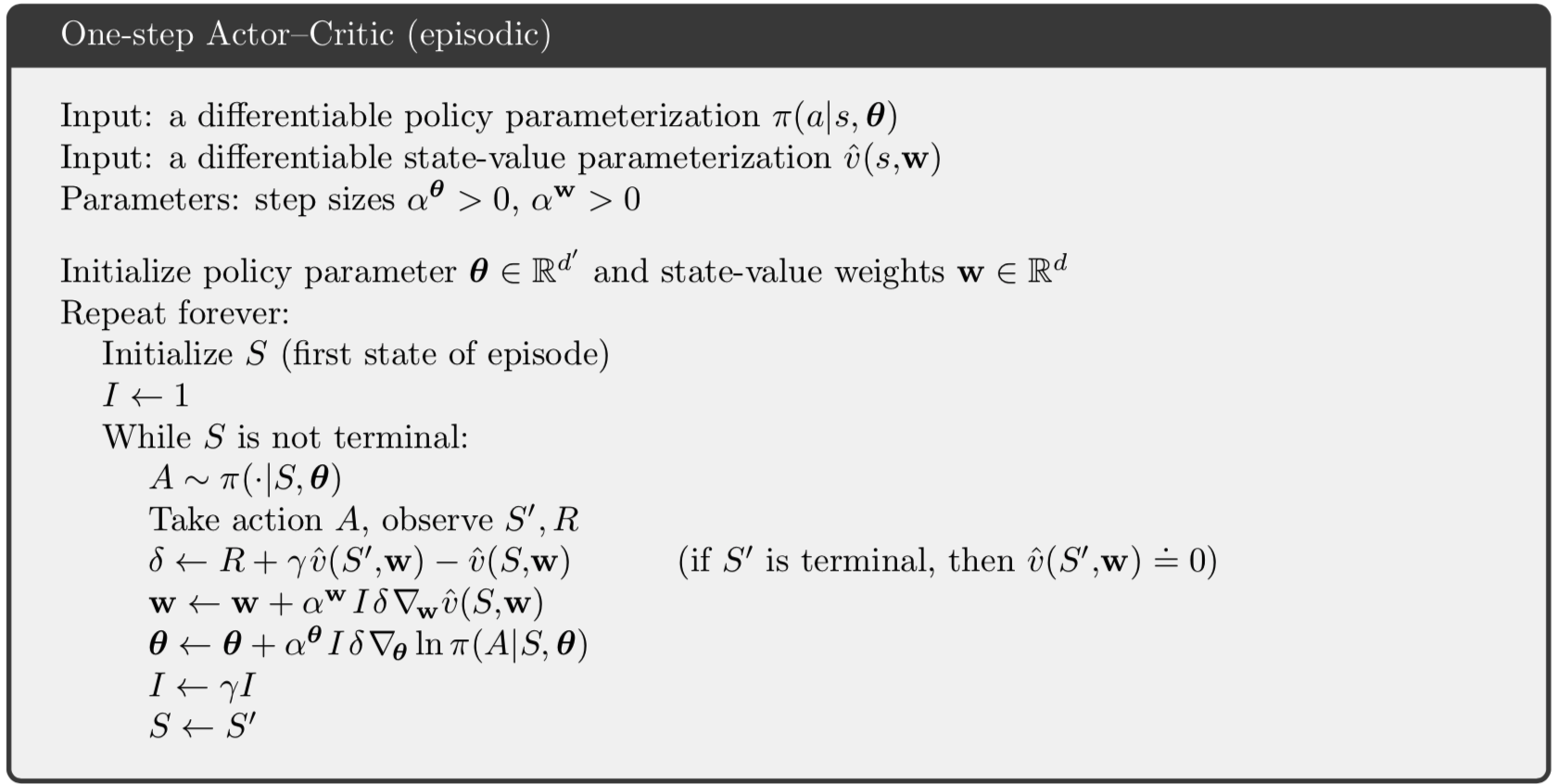
Note that Worker.train implements the loop $latex for \; i \in \{t-1, \cdots,t_{start}\}$ in the pseudocode.
 , where each
, where each 
 . (If using this criteria,
. (If using this criteria, 

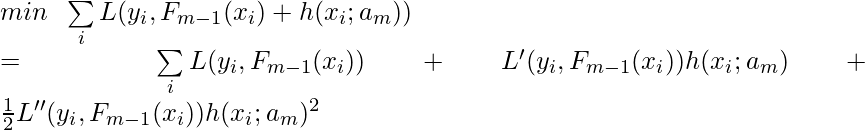
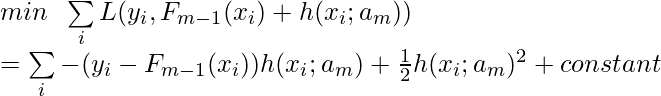

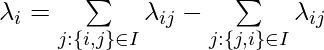

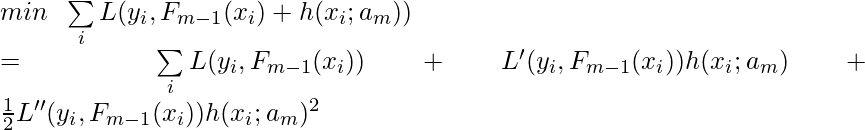








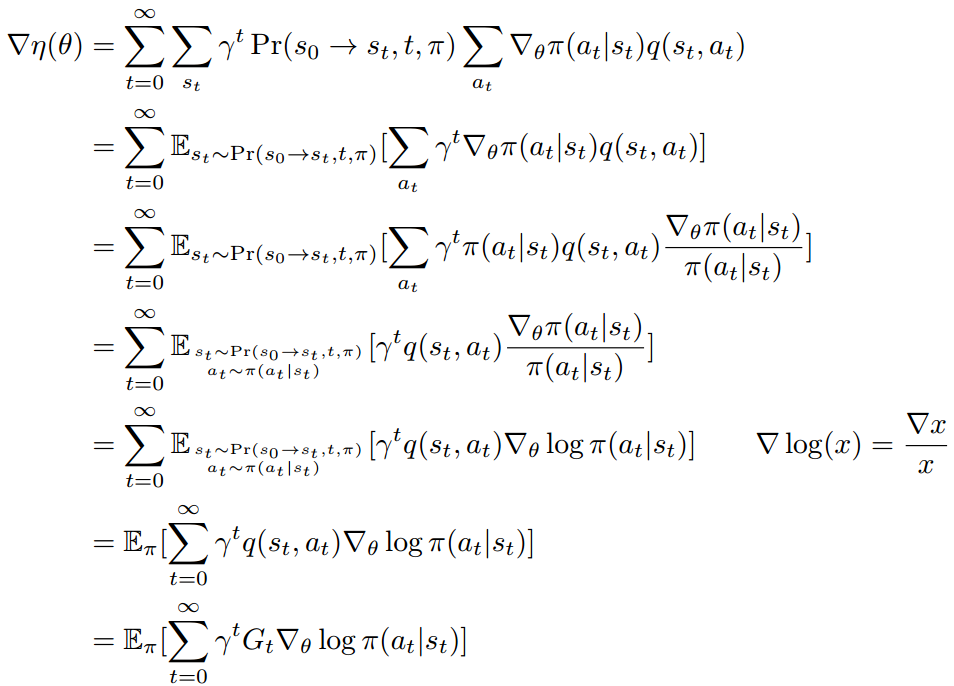
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \nabla \eta(\theta) = \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}}[\sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t|s_t)] &s=2](https://czxttkl.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-093ef803c0ca0df70cae9b9ecec84de5_l3.png)

![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [\sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t (G_t - b(s_t)) \nabla_\theta \log \pi (a_t|s_t)]](https://czxttkl.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8d586d2f867e3a9f19be27fbca1afe2b_l3.png) is an unbiased estimate of
is an unbiased estimate of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}}[\sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t b(s_t) \nabla_\theta \log \pi (a_t | s_t)]](https://czxttkl.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-39cb9ee96a8a70267a3c0f0de4ba410e_l3.png) is not zero.
is not zero.![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com Var[ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)]](https://czxttkl.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-00b7d15eb73cf2b088fdad5a69ff16ac_l3.png) .
.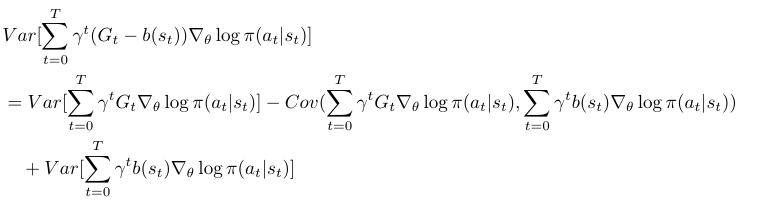
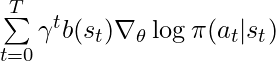 has large enough covariance with
has large enough covariance with 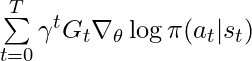 to outweigh its own variance, then the variance is reduced. Unrealistically, if
to outweigh its own variance, then the variance is reduced. Unrealistically, if 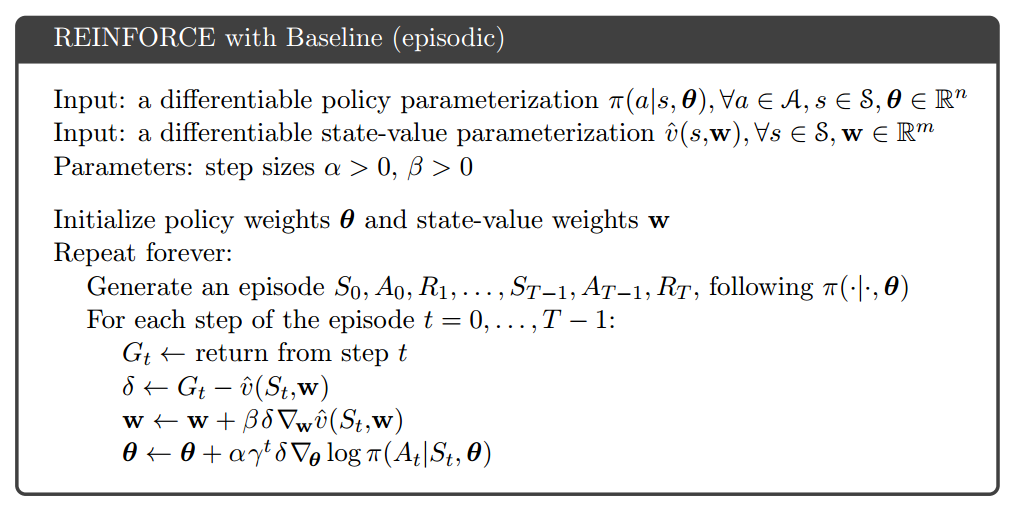
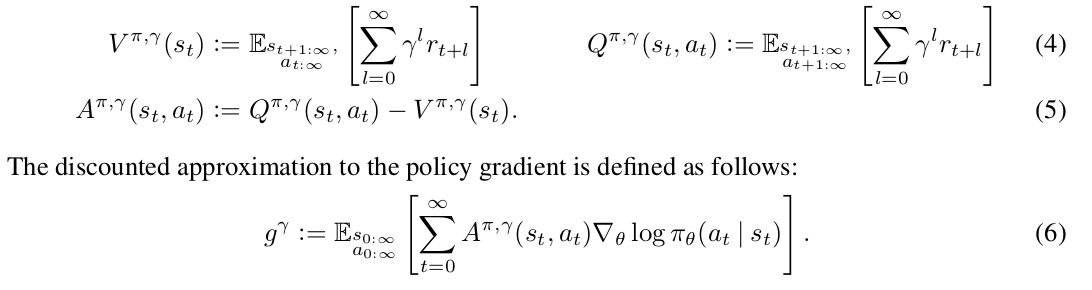
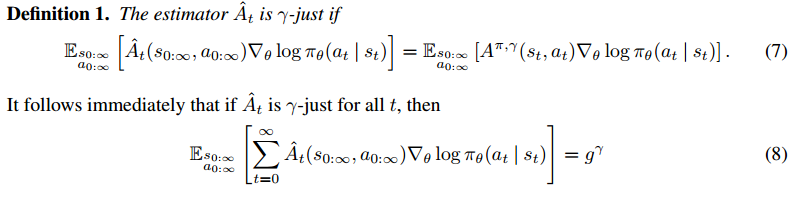
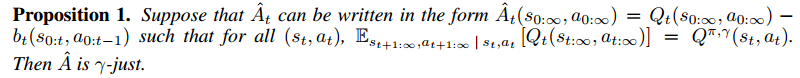
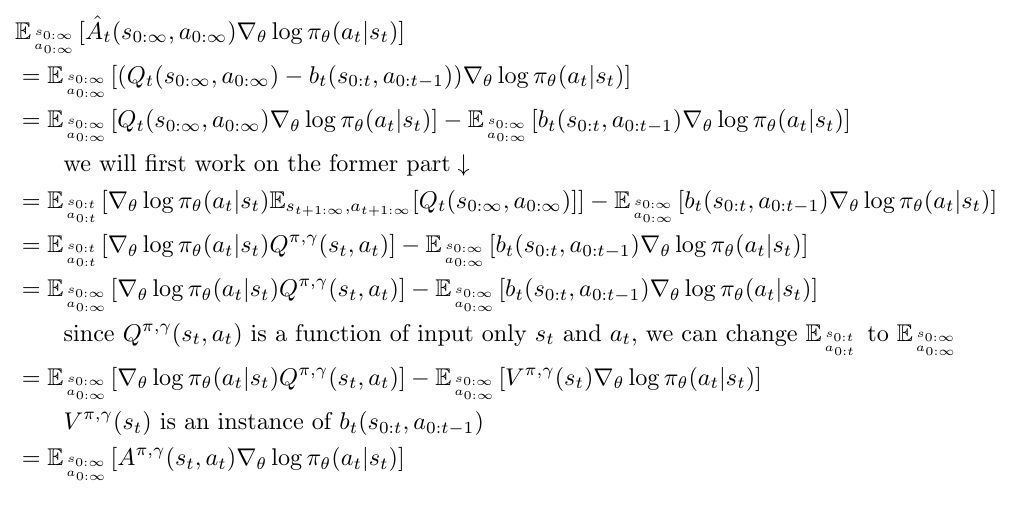
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{align*} \nabla \eta(\theta) &= \nabla_\theta v_{\pi} (s_0) \quad \quad \text{performance measure is the value of starting state} \\ &= \nabla_\theta \big[ \sum\limits_{a_0} \pi(a_0|s_0) q(s_0,a_0) \big] \\ &=\sum\limits_{a_0} \big[ \nabla_\theta \pi(a_0|s_0) q(s_0, a_0) + \pi(a_0|s_0) \nabla_\theta q(s_0, a_0) \big] \quad \quad \text{derivative product rule} \\ &= \sum\limits_{a_0} \Big[ \nabla_\theta \pi(a_0|s_0) q(s_0, a_0) + \pi(a_0|s_0) \nabla_\theta \big[ \sum\limits_{s_1,r_0} p(s_1, r_0 |s_0,a_0)(r_0 + \gamma v_\pi(s_1)) \big] \Big] \\ &= \sum\limits_{a_0} \big[ \nabla_\theta \pi (a_0 | s_0) q(s_0, a_0) + \pi(a_0 | s_0) \sum\limits_{s_1} \gamma p(s_1| s_0, a_0) \nabla_\theta v_{\pi}(s_1) \big] \qquad r \text{ has nothing to do with regard to } \theta \\ & \qquad \text{up till now, we have a recursion:} \\ & \qquad \nabla_\theta v_\pi(s_t)= \sum\limits_{a_t} \Big[ \nabla_\theta \pi(a_t|s_t) q(s_t, a_t) + \pi(a_t|s_t) \big[ \sum\limits_{s_{t+1}} \gamma p(s_{t+1}|s_t,a_t) \nabla_\theta v_\pi(s_{t+1}) \big] \Big] \\ &=\sum\limits_{a_0} \Big[ \nabla_\theta \pi (a_0 | s_0) q(s_0, a_0) + \pi(a_0 | s_0) \sum\limits_{s_1} \gamma p(s_1| s_0, a_0) \\ & \qquad \qquad \sum\limits_{a_1} \big[ \nabla_\theta \pi(a_1 | s_1)q(s_1, a_1) + \pi(a_1 | s_1)\sum\limits_{s_2} \gamma p(s_2|s_1, a_1) \nabla_\theta v_{\pi} (s_2) \big] \Big] \\ &=\sum\limits_{a_0} \nabla_\theta \pi (a_0 | s_0) q(s_0, a_0) \\ & \qquad + \gamma \sum\limits_{s_1} \sum\limits_{a_0} p(s_1| s_0, a_0) \pi(a_0 | s_0) \sum\limits_{a_1} \nabla_\theta \pi(a_1 | s_1)q(s_1, a_1) \\ & \qquad + \gamma^2 \sum\limits_{s_2} \sum\limits_{a_1} \sum\limits_{s_1} \sum\limits_{a_0} p(s_2|s_1, a_1) \pi(a_1 | s_1) p(s_1| s_0, a_0) \pi(a_0 | s_0) \nabla_\theta v_{\pi} (s_2) \\ &= \cdots \qquad \text{(keep unrolling using the recursion)}\\ &= \sum\limits_{t=0}^\infty \sum\limits_{s_t} \gamma^t \Pr(s_0 \rightarrow s_t, t, \pi) \sum\limits_{a_t} \nabla_\theta \pi(a_t | s_t) q(s_t, a_t) \qquad \Pr(s_0 \rightarrow s_t, t, \pi) \text{ is the prob. of } s_0 \text{ to } s_t \text{ in } t \text{ steps} \end{align*}](https://czxttkl.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8ade309cbfbab77fb5d741c4ea3a7df6_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{align*} \nabla \eta(\theta) &= \sum\limits_{t=0}^\infty \sum\limits_{s_t} \gamma^t \Pr(s_0 \rightarrow s_t, t, \pi) \sum\limits_{a_t} \nabla_\theta \pi(a_t | s_t) q(s_t, a_t) \\ &=\sum\limits_{t=0}^\infty \mathbb{E}_{s_t \sim \Pr(s_0 \rightarrow s_t, t, \pi)}[\sum\limits_{a_t} \gamma^t \nabla_\theta \pi(a_t | s_t) q(s_t, a_t) ] \\ &=\sum\limits_{t=0}^\infty \mathbb{E}_{s_t \sim \Pr(s_0 \rightarrow s_t, t, \pi)} [\sum\limits_{a_t} \gamma^t \pi(a_t | s_t) q(s_t, a_t) \frac{\nabla_\theta \pi(a_t | s_t)}{\pi(a_t | s_t)} ] \\ &=\sum\limits_{t=0}^\infty \mathbb{E}_{s_t \sim \Pr(s_0 \rightarrow s_t, t, \pi) \atop a_t \sim \pi(a_t | s_t) \quad}[ \gamma^t q(s_t, a_t) \frac{\nabla_\theta \pi(a_t | s_t)}{\pi(a_t | s_t)}] \\ &=\sum\limits_{t=0}^\infty \mathbb{E}_{s_t \sim \Pr(s_0 \rightarrow s_t, t, \pi) \atop a_t \sim \pi(a_t | s_t) \quad}[ \gamma^t q(s_t, a_t) \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] \qquad \nabla \log(x) = \frac{\nabla x}{x} \\ &=\mathbb{E}_{\pi}[ \sum\limits_{t=0}^\infty \gamma^t q(s_t, a_t) \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] \\ &=\mathbb{E}_{\pi}[ \sum\limits_{t=0}^\infty \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] \end{align*}](https://czxttkl.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d532fc2a9f8b3c450bf990553854353e_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{align*} &\mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t (G_t - b(s_t)) \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] \\ =& \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] - \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}}[ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t b(s_t) \nabla_\theta \log \pi (a_t | s_t) ] \\ =& \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] - \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}}[ \gamma^t b(s_t) \nabla_\theta \log \pi (a_t | s_t) ] \qquad \text{exp. of sum equals to sum of exp.}\\ =& \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] - \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \mathbb{E}_{s_{t}, a_{t}}[ \gamma^t b(s_t) \nabla_\theta \log \pi (a_t | s_t) ] \qquad \text{remove irrelevant variables in each exp.}\\ =& \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] - \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \sum\limits_{s_{t}} \sum\limits_{a_{t}} p(s_t, a_t) \gamma^t b(s_t) \nabla_\theta \log \pi (a_t | s_t) \qquad \text{expectation form} \rightarrow \text{discrete sum} \\ =& \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] - \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \sum\limits_{s_{t}} \sum\limits_{a_{t}} p(s_t) \pi(a_t|s_t) \gamma^t b(s_t) \frac{\nabla_\theta \pi (a_t | s_t)}{\pi(a_t | s_t) } \qquad \text{rule of probability} \\ =& \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] - \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \sum\limits_{s_{t}} \gamma^t b(s_t) p(s_t) \sum\limits_{a_{t}} \nabla_\theta \pi (a_t | s_t) \\ =& \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] - \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \sum\limits_{s_{t}} \gamma^t b(s_t) p(s_t) \nabla_\theta \sum\limits_{a_{t}} \pi (a_t | s_t) \\ =& \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] - \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \sum\limits_{s_{t}} \gamma^t b(s_t) p(s_t) \nabla_\theta 1 \\ =& \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:T}, a_{0:T}} [ \sum\limits_{t=0}^T \gamma^t G_t \nabla_\theta \log \pi(a_t | s_t)] \\ =& \nabla \eta(\theta) \end{align*}](https://czxttkl.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b260de314aa5bf15c7507b755c32d260_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{align*} &\mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}} [\hat{A}_t(s_{0:\infty}, a_{0:\infty}) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t) ] \\ &= \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}} [(Q_t(s_{0:\infty}, a_{0:\infty}) - b_t(s_{0:t}, a_{0:t-1})) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t)] \\ &= \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}}[Q_t(s_{0:\infty}, a_{0:\infty}) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t)] - \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}}[b_t(s_{0:t}, a_{0:t-1}) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t)] \\ &\qquad \text{we will first work on the former part} \downarrow \\ &= \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:t} \atop a_{0:t}}[\nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t) \mathbb{E}_{s_{t+1:\infty}, a_{t+1:\infty}} [Q_t(s_{0:\infty}, a_{0:\infty})] ] - \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}}[b_t(s_{0:t}, a_{0:t-1}) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t)] \\ &= \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:t} \atop a_{0:t}}[\nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t) Q^{\pi, \gamma}(s_t, a_t)] - \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}}[b_t(s_{0:t}, a_{0:t-1}) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t)] \\ &= \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}}[\nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t) Q^{\pi, \gamma}(s_t, a_t)] - \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}}[b_t(s_{0:t}, a_{0:t-1}) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t)] \\ &\qquad \text{since } Q^{\pi, \gamma}(s_t, a_t) \text{ is a function of input only } s_t \text{ and } a_t \text{, we can change } \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:t} \atop a_{0:t}} \text{ to } \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}} \\ &= \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}}[\nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t) Q^{\pi, \gamma}(s_t, a_t)] - \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}}[V^{\pi, \gamma}(s_t) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t)] \\ &\qquad V^{\pi, \gamma}(s_t) \text{ is an instance of } b_t(s_{0:t}, a_{0:t-1}) \\ &= \mathbb{E}_{s_{0:\infty} \atop a_{0:\infty}} [A^{\pi, \gamma}(s_t, a_t) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(a_t | s_t) ] \end{align*}](https://czxttkl.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-fa43561b5bd4e04c093fa2ab3b2d81b9_l3.png)