In this post, I am doing a brief code walkthrough for the code written in https://medium.com/emergent-future/simple-reinforcement-learning-with-tensorflow-part-8-asynchronous-actor-critic-agents-a3c-c88f72a5e9f2
The code implements A3C algorithm (Asynchronous Methods for Deep Reinforcement Learning). It follows the pseudocode given in supplemental part in the paper:
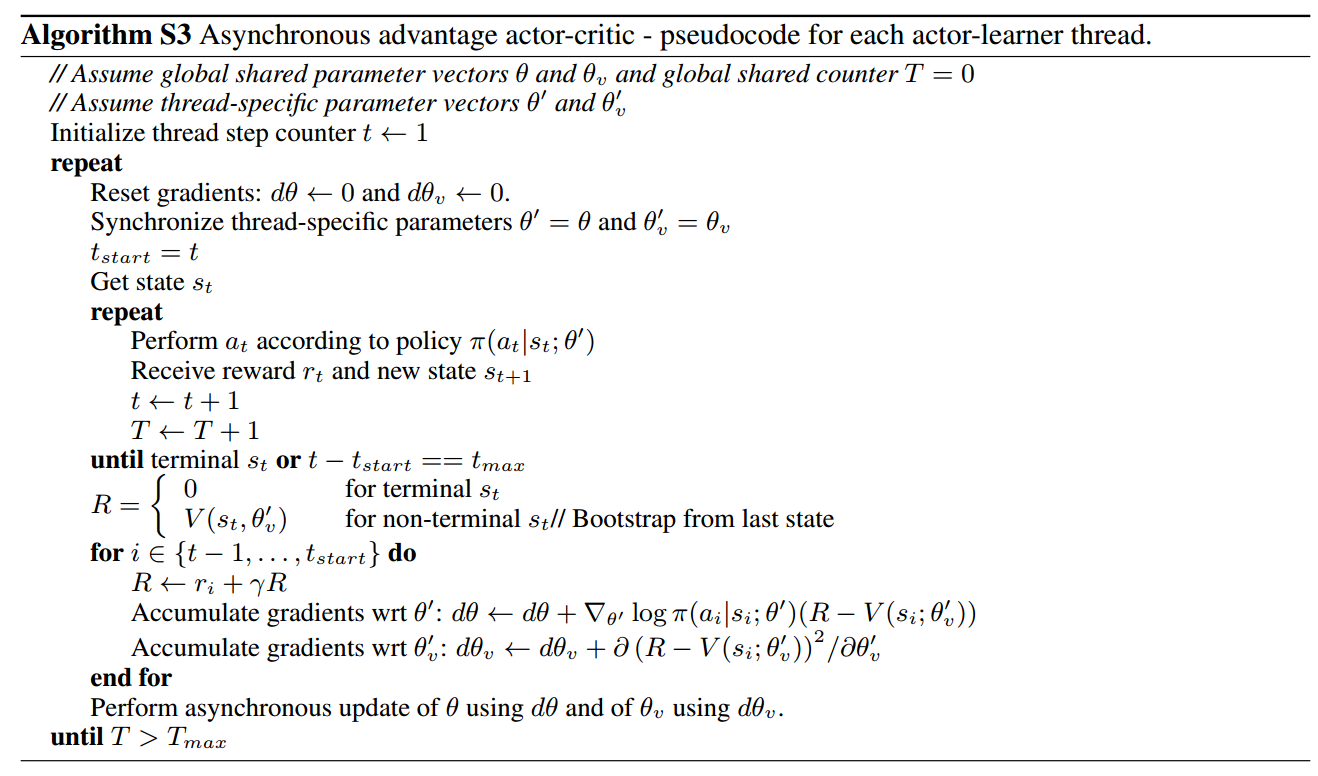
The structure of this model is:
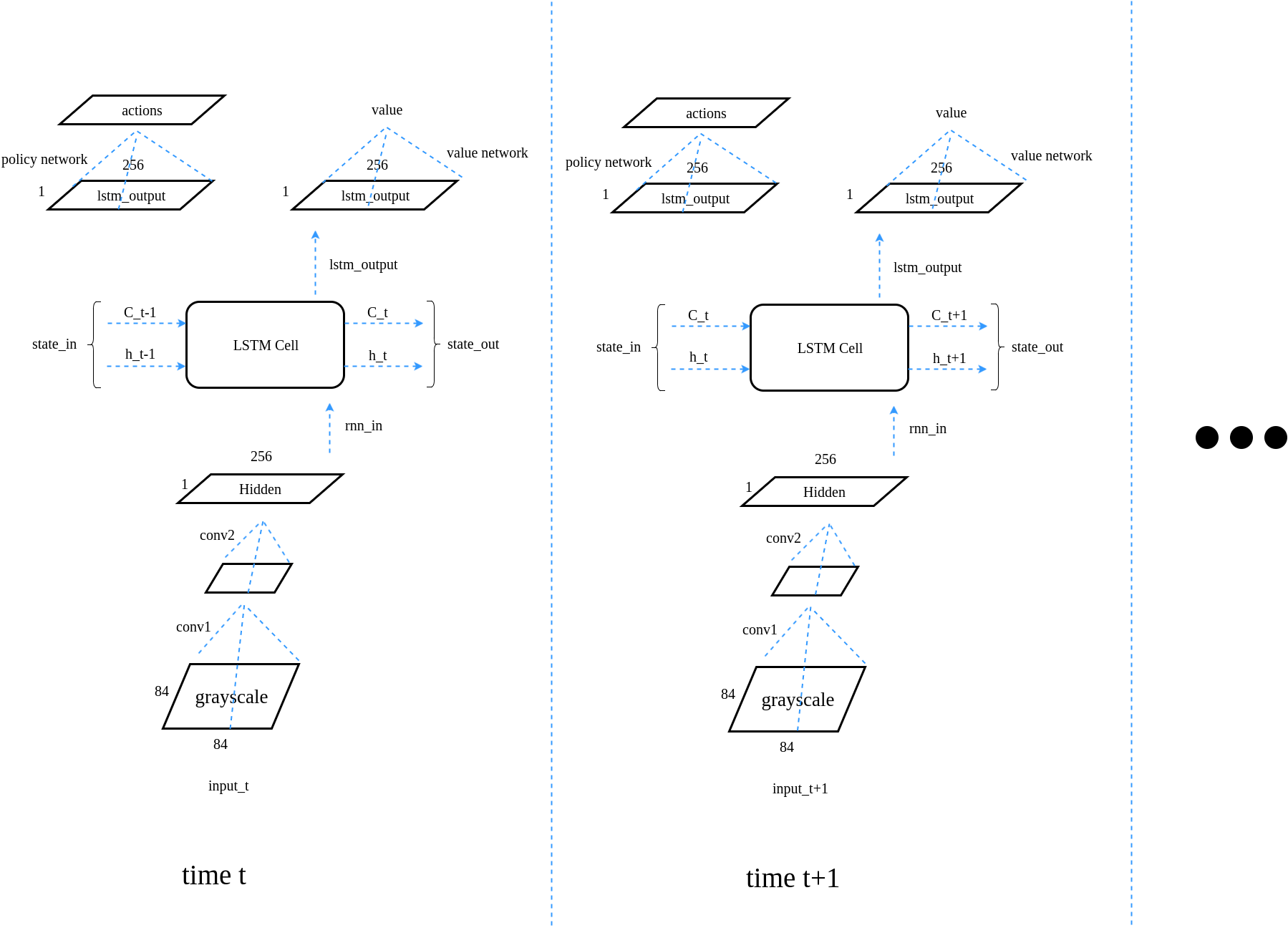
For LSTM structure detail, refer to http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/. I am using the same notation in the model structure diagram as in the link.
Below is the code:
"""
Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic algorithm
See:
https://medium.com/emergent-future/simple-reinforcement-learning-with-tensorflow-part-8-asynchronous-actor-critic-agents-a3c-c88f72a5e9f2
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1602.01783.pdf
"""
import copy
import threading
import multiprocessing
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim
import scipy.signal
from helper import *
from vizdoom import *
from random import choice
from time import sleep
from time import time
# Copies one set of variables to another.
# Used to set worker network parameters to those of global network.
def update_target_graph(from_scope,to_scope):
from_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, from_scope)
to_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, to_scope)
op_holder = []
for from_var,to_var in zip(from_vars,to_vars):
op_holder.append(to_var.assign(from_var))
return op_holder
# Processes Doom screen image to produce cropped and resized image.
def process_frame(frame):
s = frame[10:-10,30:-30]
s = scipy.misc.imresize(s,[84,84])
s = np.reshape(s,[np.prod(s.shape)]) / 255.0
return s
# Discounting function used to calculate discounted returns.
def discount(x, gamma):
return scipy.signal.lfilter([1], [1, -gamma], x[::-1], axis=0)[::-1]
#Used to initialize weights for policy and value output layers
def normalized_columns_initializer(std=1.0):
def _initializer(shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None):
out = np.random.randn(*shape).astype(np.float32)
out *= std / np.sqrt(np.square(out).sum(axis=0, keepdims=True))
return tf.constant(out)
return _initializer
class AC_Network():
def __init__(self, s_size, a_size, scope, trainer):
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
# Input and visual encoding layers
self.inputs = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, s_size], dtype=tf.float32)
self.imageIn = tf.reshape(self.inputs, shape=[-1, 84, 84, 1])
self.conv1 = slim.conv2d(activation_fn=tf.nn.elu,
inputs=self.imageIn, num_outputs=16,
kernel_size=[8, 8], stride=[4, 4], padding='VALID')
self.conv2 = slim.conv2d(activation_fn=tf.nn.elu,
inputs=self.conv1, num_outputs=32,
kernel_size=[4, 4], stride=[2, 2], padding='VALID')
hidden = slim.fully_connected(slim.flatten(self.conv2), 256, activation_fn=tf.nn.elu)
# Recurrent network for temporal dependencies
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(256, state_is_tuple=True)
self.lstm_cell_c_size = lstm_cell.state_size.c
self.lstm_cell_h_size = lstm_cell.state_size.h
c_init = np.zeros((1, lstm_cell.state_size.c), np.float32)
h_init = np.zeros((1, lstm_cell.state_size.h), np.float32)
self.state_init = [c_init, h_init]
c_in = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [1, lstm_cell.state_size.c])
h_in = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [1, lstm_cell.state_size.h])
self.state_in = (c_in, h_in)
rnn_in = tf.expand_dims(hidden, [0])
step_size = tf.shape(self.imageIn)[:1]
state_in = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMStateTuple(c_in, h_in)
lstm_outputs, lstm_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(
lstm_cell, rnn_in, initial_state=state_in, sequence_length=step_size,
time_major=False)
lstm_c, lstm_h = lstm_state
self.state_out = (lstm_c[:1, :], lstm_h[:1, :])
rnn_out = tf.reshape(lstm_outputs, [-1, 256])
# Output layers for policy and value estimations
self.policy = slim.fully_connected(rnn_out, a_size,
activation_fn=tf.nn.softmax,
weights_initializer=normalized_columns_initializer(0.01),
biases_initializer=None)
self.value = slim.fully_connected(rnn_out, 1,
activation_fn=None,
weights_initializer=normalized_columns_initializer(1.0),
biases_initializer=None)
# Only the worker network need ops for loss functions and gradient updating.
if scope != 'global':
self.actions = tf.placeholder(shape=[None], dtype=tf.int32)
self.actions_onehot = tf.one_hot(self.actions, a_size, dtype=tf.float32)
self.target_v = tf.placeholder(shape=[None], dtype=tf.float32)
self.advantages = tf.placeholder(shape=[None], dtype=tf.float32)
self.responsible_outputs = tf.reduce_sum(self.policy * self.actions_onehot, [1])
# Loss functions
self.value_loss = 0.5 * tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(self.target_v - tf.reshape(self.value, [-1])))
self.entropy = - tf.reduce_sum(self.policy * tf.log(self.policy))
self.policy_loss = -tf.reduce_sum(tf.log(self.responsible_outputs) * self.advantages)
self.loss = 0.5 * self.value_loss + self.policy_loss - self.entropy * 0.01
# Get gradients from local network using local losses
local_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope)
self.gradients = tf.gradients(self.loss, local_vars)
self.var_norms = tf.global_norm(local_vars)
grads, self.grad_norms = tf.clip_by_global_norm(self.gradients, 40.0)
# Apply local gradients to global network
global_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, 'global')
self.apply_grads = trainer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, global_vars))
def state_in_init(self):
c_init = np.zeros((1, self.lstm_cell_c_size), np.float32)
h_init = np.zeros((1, self.lstm_cell_h_size), np.float32)
self.state_init = [c_init, h_init]
class Worker():
def __init__(self, game, name, s_size, a_size, trainer, model_path, global_episodes):
self.name = "worker_" + str(name)
self.number = name
self.model_path = model_path
self.trainer = trainer
self.global_episodes = global_episodes
self.increment = self.global_episodes.assign_add(1)
self.episode_rewards = []
self.episode_lengths = []
self.episode_mean_values = []
self.summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("train_" + str(self.number))
# Create the local copy of the network and the tensorflow op to copy global paramters to local network
self.local_AC = AC_Network(s_size, a_size, self.name, trainer)
self.update_local_ops = update_target_graph('global', self.name)
# The Below code is related to setting up the Doom environment
game.set_doom_scenario_path("basic.wad") # This corresponds to the simple task we will pose our agent
game.set_doom_map("map01")
game.set_screen_resolution(ScreenResolution.RES_160X120)
game.set_screen_format(ScreenFormat.GRAY8)
game.set_render_hud(False)
game.set_render_crosshair(False)
game.set_render_weapon(True)
game.set_render_decals(False)
game.set_render_particles(False)
game.add_available_button(Button.MOVE_LEFT)
game.add_available_button(Button.MOVE_RIGHT)
game.add_available_button(Button.ATTACK)
game.add_available_game_variable(GameVariable.AMMO2)
game.add_available_game_variable(GameVariable.POSITION_X)
game.add_available_game_variable(GameVariable.POSITION_Y)
game.set_episode_timeout(300)
game.set_episode_start_time(10)
game.set_window_visible(False)
game.set_sound_enabled(False)
game.set_living_reward(-1)
game.set_mode(Mode.PLAYER)
game.init()
self.actions = np.identity(a_size, dtype=bool).tolist()
# End Doom set-up
self.env = game
def train(self, rollout, sess, gamma, bootstrap_value):
rollout = np.array(rollout)
observations = rollout[:, 0]
actions = rollout[:, 1]
rewards = rollout[:, 2]
next_observations = rollout[:, 3]
values = rollout[:, 5]
# Here we take the rewards and values from the rollout, and use them to
# generate the advantage and discounted returns.
# The advantage function uses "Generalized Advantage Estimation"
self.rewards_plus = np.asarray(rewards.tolist() + [bootstrap_value])
discounted_rewards = discount(self.rewards_plus, gamma)[:-1]
self.value_plus = np.asarray(values.tolist() + [bootstrap_value])
advantages = rewards + gamma * self.value_plus[1:] - self.value_plus[:-1]
advantages = discount(advantages, gamma)
# Update the global network using gradients from loss
# Generate network statistics to periodically save
rnn_state = self.local_AC.state_init
feed_dict = {self.local_AC.target_v: discounted_rewards,
self.local_AC.inputs: np.vstack(observations),
self.local_AC.actions: actions,
self.local_AC.advantages: advantages,
self.local_AC.state_in[0]: rnn_state[0],
self.local_AC.state_in[1]: rnn_state[1]}
v_l, p_l, e_l, g_n, v_n, _ = sess.run([self.local_AC.value_loss,
self.local_AC.policy_loss,
self.local_AC.entropy,
self.local_AC.grad_norms,
self.local_AC.var_norms,
self.local_AC.apply_grads],
feed_dict=feed_dict)
return v_l / len(rollout), p_l / len(rollout), e_l / len(rollout), g_n, v_n
def work(self, max_episode_length, gamma, sess, coord, saver):
episode_count = sess.run(self.global_episodes)
total_steps = 0
print("Starting worker " + str(self.number))
with sess.as_default(), sess.graph.as_default():
while not coord.should_stop():
# copy global network parameter to self parameter
sess.run(self.update_local_ops)
# when a new episode starts, C_0 & h_0 of LSTM are reset to zero
self.local_AC.state_in_init()
episode_buffer = []
episode_values = []
episode_frames = []
episode_reward = 0
episode_step_count = 0
d = False
self.env.new_episode()
s = self.env.get_state().screen_buffer
episode_frames.append(s)
s = process_frame(s)
rnn_state = self.local_AC.state_init
while self.env.is_episode_finished() == False:
# Take an action using probabilities from policy network output.
# after this step, a_dist shape (1,3), v shape (1,1),
# rnn_state: first array (C): (1, 256), second array (h): (1, 256)
a_dist, v, rnn_state = sess.run(
[self.local_AC.policy, self.local_AC.value, self.local_AC.state_out],
feed_dict={self.local_AC.inputs: [s],
self.local_AC.state_in[0]: rnn_state[0],
self.local_AC.state_in[1]: rnn_state[1]})
a = np.random.choice(a_dist[0], p=a_dist[0])
a = np.argmax(a_dist == a) # return the best action index
# see http://vizdoom.cs.put.edu.pl/tutorial and
# https://github.com/mwydmuch/ViZDoom/blob/3bdb16935668aa42bb14cc38ac397b8954999cca/doc/DoomGame.md
# for reward description
# the agent gets rewards for each action which is -1 for each time tick,
# -6 if he shots but misses, and 100 if he kills the monster
r = self.env.make_action(self.actions[a]) / 100.0 # make_action returns reward
# In this example, the episode finishes after 300 tics or when the monster gets killed
# ref: http://www.cs.put.poznan.pl/visualdoomai/tutorial.html#basic - Game Runtime
d = self.env.is_episode_finished()
if d == False:
s1 = self.env.get_state().screen_buffer
episode_frames.append(s1)
s1 = process_frame(s1)
else:
s1 = s
episode_buffer.append([s, a, r, s1, d, v[0, 0]])
episode_values.append(v[0, 0])
episode_reward += r
s = s1
total_steps += 1
episode_step_count += 1
# If the episode hasn't ended, but the experience buffer is full, then we
# make an update step using that experience rollout.
if len(episode_buffer) == 30 and d != True and episode_step_count != max_episode_length - 1:
# Since we don't know what the true final return is, we "bootstrap" from our current
# value estimation.
v1 = sess.run(self.local_AC.value,
feed_dict={self.local_AC.inputs: [s],
self.local_AC.state_in[0]: rnn_state[0],
self.local_AC.state_in[1]: rnn_state[1]})
v1 = v1[0, 0]
v_l, p_l, e_l, g_n, v_n = self.train(episode_buffer, sess, gamma, v1)
episode_buffer = []
sess.run(self.update_local_ops)
# original code does not update state_init:
# in train function, rnn_state is always set to self.state_init which are two zero numpy arrays
self.local_AC.state_init = copy.deepcopy(rnn_state)
if d == True:
break
self.episode_rewards.append(episode_reward)
self.episode_lengths.append(episode_step_count)
self.episode_mean_values.append(np.mean(episode_values))
# Update the network using the experience buffer at the end of the episode.
if len(episode_buffer) != 0:
v_l, p_l, e_l, g_n, v_n = self.train(episode_buffer, sess, gamma, 0.0)
# Periodically save gifs of episodes, model parameters, and summary statistics.
if episode_count % 5 == 0 and episode_count != 0:
if self.name == 'worker_0' and episode_count % 25 == 0:
time_per_step = 0.05
images = np.array(episode_frames)
make_gif(images, './frames/image' + str(episode_count) + '.gif',
duration=len(images) * time_per_step, true_image=True, salience=False)
if episode_count % 250 == 0 and self.name == 'worker_0':
saver.save(sess, self.model_path + '/model-' + str(episode_count) + '.cptk')
print("Saved Model")
mean_reward = np.mean(self.episode_rewards[-5:])
mean_length = np.mean(self.episode_lengths[-5:])
mean_value = np.mean(self.episode_mean_values[-5:])
summary = tf.Summary()
summary.value.add(tag='Perf/Reward', simple_value=float(mean_reward))
summary.value.add(tag='Perf/Length', simple_value=float(mean_length))
summary.value.add(tag='Perf/Value', simple_value=float(mean_value))
summary.value.add(tag='Losses/Value Loss', simple_value=float(v_l))
summary.value.add(tag='Losses/Policy Loss', simple_value=float(p_l))
summary.value.add(tag='Losses/Entropy', simple_value=float(e_l))
summary.value.add(tag='Losses/Grad Norm', simple_value=float(g_n))
summary.value.add(tag='Losses/Var Norm', simple_value=float(v_n))
self.summary_writer.add_summary(summary, episode_count)
self.summary_writer.flush()
if self.name == 'worker_0':
sess.run(self.increment)
episode_count += 1
max_episode_length = 300
gamma = .99 # discount rate for advantage estimation and reward discounting
s_size = 7056 # Observations are greyscale frames of 84 * 84 * 1
a_size = 3 # Agent can move Left, Right, or Fire
load_model = False
model_path = './model'
tf.reset_default_graph()
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
os.makedirs(model_path)
# Create a directory to save episode playback gifs to
if not os.path.exists('./frames'):
os.makedirs('./frames')
with tf.device("/cpu:0"):
global_episodes = tf.Variable(0, dtype=tf.int32, name='global_episodes', trainable=False)
trainer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=1e-4)
master_network = AC_Network(s_size, a_size, 'global', None) # Generate global network
num_workers = multiprocessing.cpu_count() # Set workers ot number of available CPU threads
workers = []
# Create worker classes
for i in range(num_workers):
workers.append(Worker(DoomGame(), i, s_size, a_size, trainer, model_path, global_episodes))
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=5)
with tf.Session() as sess:
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
if load_model == True:
print('Loading Model...')
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(model_path)
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
else:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# This is where the asynchronous magic happens.
# Start the "work" process for each worker in a separate threat.
worker_threads = []
for worker in workers:
worker_work = lambda: worker.work(max_episode_length, gamma, sess, coord, saver)
t = threading.Thread(target=(worker_work))
t.start()
sleep(0.5)
worker_threads.append(t)
coord.join(worker_threads)
Note that Worker.train implements the loop $latex for \; i \in \{t-1, \cdots,t_{start}\}$ in the pseudocode.